You are website owner/developer and you need to increase website speed and less loading time, You junst need to add below .htaccess script :
Linux Server——————————————-
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
Options +FollowSymLinks
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteRule ^ index.php [L]
</IfModule>
# BEGIN WordPress
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteRule ^index\.php$ – [L]
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule . /index.php [L]
</IfModule>
# END WordPress
<IfModule mod_deflate.c>
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/html
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/css
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/javascript
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/xml
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/plain
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE image/x-icon
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE image/svg+xml
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/rss+xml
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/javascript
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/x-javascript
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/xml
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/xhtml+xml
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/x-font
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/x-font-truetype
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/x-font-ttf
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/x-font-otf
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/x-font-opentype
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/vnd.ms-fontobject
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE font/ttf
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE font/otf
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE font/opentype
# For Olders Browsers Which Can’t Handle Compression
BrowserMatch ^Mozilla/4 gzip-only-text/html
BrowserMatch ^Mozilla/4\.0[678] no-gzip
BrowserMatch \bMSIE !no-gzip !gzip-only-text/html
</IfModule>
<ifModule mod_gzip.c>
mod_gzip_on Yes
mod_gzip_dechunk Yes
mod_gzip_item_include file \.(html?|txt|css|js|php|pl)$
mod_gzip_item_include mime ^application/x-javascript.*
mod_gzip_item_include mime ^text/.*
mod_gzip_item_exclude rspheader ^Content-Encoding:.*gzip.*
mod_gzip_item_exclude mime ^image/.*
mod_gzip_item_include handler ^cgi-script$
</ifModule>
## EXPIRES CACHING ##
<IfModule mod_expires.c>
ExpiresActive On
ExpiresByType image/jpg “access 1 month”
ExpiresByType image/jpeg “access 1 month”
ExpiresByType image/gif “access 1 month”
ExpiresByType image/png “access 1 month”
ExpiresByType text/css “access 2 day”
ExpiresByType text/html “access 1 month”
ExpiresByType application/pdf “access 1 month”
ExpiresByType text/x-javascript “access 2 day”
ExpiresByType application/x-shockwave-flash “access 1 month”
ExpiresByType image/x-icon “access 1 month”
ExpiresDefault “access 1 month”
</IfModule>
## EXPIRES CACHING ##
———————————————
Windows Server—————————————
<?xml version=”1.0″ encoding=”utf-8″?>
<configuration>
<system.webServer>
<!– GZip static file content. Overrides the server default which only compresses static files over 2700 bytes –>
<httpCompression directory=”%SystemDrive%\websites\_compressed” minFileSizeForComp=”1024″>
<scheme name=”gzip” dll=”%Windir%\system32\inetsrv\gzip.dll” />
<staticTypes>
<add mimeType=”text/*” enabled=”true” />
<add mimeType=”message/*” enabled=”true” />
<add mimeType=”application/javascript” enabled=”true” />
<add mimeType=”application/json” enabled=”true” />
<add mimeType=”*/*” enabled=”false” />
</staticTypes>
</httpCompression>
<httpErrors existingResponse=”PassThrough” errorMode=”Custom”>
<!– Catch IIS 404 error due to paths that exist but shouldn’t be served (e.g. /controllers, /global.asax) or IIS request filtering (e.g. bin, web.config, app_code, app_globalresources, app_localresources, app_webreferences, app_data, app_browsers) –>
<remove statusCode=”404″ subStatusCode=”-1″ />
<error statusCode=”404″ subStatusCode=”-1″ path=”/notfound” responseMode=”ExecuteURL” />
<remove statusCode=”500″ subStatusCode=”-1″ />
<error statusCode=”500″ subStatusCode=”-1″ path=”/error” responseMode=”ExecuteURL” />
</httpErrors>
<directoryBrowse enabled=”false” />
<validation validateIntegratedModeConfiguration=”false” />
<!– Microsoft sets runAllManagedModulesForAllRequests to true by default
You should handle this according to need, but consider the performance hit.
Good source of reference on this matter: http://www.west-wind.com/weblog/posts/2012/Oct/25/Caveats-with-the-runAllManagedModulesForAllRequests-in-IIS-78
–>
<modules runAllManagedModulesForAllRequests=”false” />
<urlCompression doStaticCompression=”true” doDynamicCompression=”true” />
<staticContent>
<!– Set expire headers to 30 days for static content–>
<clientCache cacheControlMode=”UseMaxAge” cacheControlMaxAge=”30.00:00:00″ />
<!– use utf-8 encoding for anything served text/plain or text/html –>
<remove fileExtension=”.css” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.css” mimeType=”text/css” />
<remove fileExtension=”.js” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.js” mimeType=”text/javascript” />
<remove fileExtension=”.json” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.json” mimeType=”application/json” />
<remove fileExtension=”.rss” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.rss” mimeType=”application/rss+xml; charset=UTF-8″ />
<remove fileExtension=”.html” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.html” mimeType=”text/html; charset=UTF-8″ />
<remove fileExtension=”.xml” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.xml” mimeType=”application/xml; charset=UTF-8″ />
<!– HTML5 Audio/Video mime types–>
<remove fileExtension=”.mp3″ />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.mp3″ mimeType=”audio/mpeg” />
<remove fileExtension=”.mp4″ />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.mp4″ mimeType=”video/mp4″ />
<remove fileExtension=”.ogg” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.ogg” mimeType=”audio/ogg” />
<remove fileExtension=”.ogv” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.ogv” mimeType=”video/ogg” />
<remove fileExtension=”.webm” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.webm” mimeType=”video/webm” />
<!– Proper svg serving. Required for svg webfonts on iPad –>
<remove fileExtension=”.svg” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.svg” mimeType=”image/svg+xml” />
<remove fileExtension=”.svgz” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.svgz” mimeType=”image/svg+xml” />
<!– HTML4 Web font mime types –>
<!– Remove default IIS mime type for .eot which is application/octet-stream –>
<remove fileExtension=”.eot” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.eot” mimeType=”application/vnd.ms-fontobject” />
<remove fileExtension=”.ttf” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.ttf” mimeType=”application/x-font-ttf” />
<remove fileExtension=”.ttc” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.ttc” mimeType=”application/x-font-ttf” />
<remove fileExtension=”.otf” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.otf” mimeType=”font/opentype” />
<remove fileExtension=”.woff” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.woff” mimeType=”application/font-woff” />
<remove fileExtension=”.crx” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.crx” mimeType=”application/x-chrome-extension” />
<remove fileExtension=”.xpi” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.xpi” mimeType=”application/x-xpinstall” />
<remove fileExtension=”.safariextz” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.safariextz” mimeType=”application/octet-stream” />
<!– Flash Video mime types–>
<remove fileExtension=”.flv” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.flv” mimeType=”video/x-flv” />
<remove fileExtension=”.f4v” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.f4v” mimeType=”video/mp4″ />
<!– Assorted types –>
<remove fileExtension=”.ico” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.ico” mimeType=”image/x-icon” />
<remove fileExtension=”.webp” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.webp” mimeType=”image/webp” />
<remove fileExtension=”.htc” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.htc” mimeType=”text/x-component” />
<remove fileExtension=”.vcf” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.vcf” mimeType=”text/x-vcard” />
<remove fileExtension=”.torrent” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.torrent” mimeType=”application/x-bittorrent” />
<remove fileExtension=”.cur” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.cur” mimeType=”image/x-icon” />
<remove fileExtension=”.webapp” />
<mimeMap fileExtension=”.webapp” mimeType=”application/x-web-app-manifest+json; charset=UTF-8″ />
</staticContent>
<httpProtocol>
<customHeaders>
<!–#### SECURITY Related Headers ###
More information: https://www.owasp.org/index.php/List_of_useful_HTTP_headers
–>
<!–
# Access-Control-Allow-Origin
The ‘Access Control Allow Origin’ HTTP header is used to control which
sites are allowed to bypass same origin policies and send cross-origin requests.
Secure configuration: Either do not set this header, or return the ‘Access-Control-Allow-Origin’
header restricting it to only a trusted set of sites.
http://enable-cors.org/
<add name=”Access-Control-Allow-Origin” value=”*” />
–>
<!–
# Cache-Control
The ‘Cache-Control’ response header controls how pages can be cached
either by proxies or the users browser.
This response header can provide enhanced privacy by not caching
sensitive pages in the users browser cache.
<add name=”Cache-Control” value=”no-store, no-cache”/>
–>
<!–
# Strict-Transport-Security
The HTTP Strict Transport Security header is used to control
if the browser is allowed to only access a site over a secure connection
and how long to remember the server response for, forcing continued usage.
Note* Currently a draft standard which only Firefox and Chrome support. But is supported by sites like PayPal.
<add name=”Strict-Transport-Security” value=”max-age=15768000″/>
–>
<!–
# X-Frame-Options
The X-Frame-Options header indicates whether a browser should be allowed
to render a page within a frame or iframe.
The valid options are DENY (deny allowing the page to exist in a frame)
or SAMEORIGIN (allow framing but only from the originating host)
Without this option set the site is at a higher risk of click-jacking.
<add name=”X-Frame-Options” value=”SAMEORIGIN” />
–>
<!–
# X-XSS-Protection
The X-XSS-Protection header is used by Internet Explorer version 8+
The header instructs IE to enable its inbuilt anti-cross-site scripting filter.
If enabled, without ‘mode=block’, there is an increased risk that
otherwise non-exploitable cross-site scripting vulnerabilities may potentially become exploitable
<add name=”X-XSS-Protection” value=”1; mode=block”/>
–>
<!–
# MIME type sniffing security protection
Enabled by default as there are very few edge cases where you wouldn’t want this enabled.
Theres additional reading below; but the tldr, it reduces the ability of the browser (mostly IE)
being tricked into facilitating driveby attacks.
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ie/gg622941(v=vs.85).aspx
http://blogs.msdn.com/b/ie/archive/2008/07/02/ie8-security-part-v-comprehensive-protection.aspx
–>
<add name=”X-Content-Type-Options” value=”nosniff” />
<!– A little extra security (by obscurity), removings fun but adding your own is better –>
<remove name=”X-Powered-By” />
<add name=”X-Powered-By” value=”My Little Pony” />
<!–//#### SECURITY Related Headers ###–>
<!–
# E-TAGS
E-Tags are actually quite useful in cache management especially if you have a front-end caching server
such as Varnish. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HTTP_ETag / http://developer.yahoo.com/performance/rules.html#etags
But in load balancing and simply most cases ETags are mishandled in IIS; and it can be advantageous to remove them.
This is simply done by overriding the default server header with an empty tag.
See http://bytestopshere.wordpress.com/2009/02/02/disable-remove-etags-on-iis-6-to-improve-performance/
<add name=”ETAG” value=”” />
–>
<!–
Force the latest IE version, in various cases when it may fall back to IE7 mode
github.com/rails/rails/commit/123eb25#commitcomment-118920
Use ChromeFrame if it’s installed for a better experience for the poor IE folk
–>
<add name=”X-UA-Compatible” value=”IE=Edge,chrome=1″ />
<!–
Allow cookies to be set from iframes (for IE only)
If needed, uncomment and specify a path or regex in the Location directive
<add name=”P3P” value=”policyref="/w3c/p3p.xml", CP="IDC DSP COR ADM DEVi TAIi PSA PSD IVAi IVDi CONi HIS OUR IND CNT"” />
–>
</customHeaders>
</httpProtocol>
<!–
<rewrite>
<rules>
Remove/force the WWW from the URL.
Requires IIS Rewrite module http://learn.iis.net/page.aspx/460/using-the-url-rewrite-module/
Configuration lifted from http://nayyeri.net/remove-www-prefix-from-urls-with-url-rewrite-module-for-iis-7-0
NOTE* You need to install the IIS URL Rewriting extension (Install via the Web Platform Installer)
http://www.microsoft.com/web/downloads/platform.aspx
** Important Note
using a non-www version of a webpage will set cookies for the whole domain making cookieless domains
(eg. fast cdn-like access of static resources like css, js and images) impossible.
# IMPORTANT: THERE ARE TWO RULES LISTED. NEVER USE BOTH RULES AT THE SAME TIME!
<rule name=”Remove WWW” stopProcessing=”true”>
<match url=”^(.*)$” />
<conditions>
<add input=”{HTTP_HOST}” pattern=”^(www\.)(.*)$” />
</conditions>
<action type=”Redirect” url=”http://example.com{PATH_INFO}” redirectType=”Permanent” />
</rule>
<rule name=”Force WWW” stopProcessing=”true”>
<match url=”.*” />
<conditions>
<add input=”{HTTP_HOST}” pattern=”^example.com$” />
</conditions>
<action type=”Redirect” url=”http://www.example.com/{R:0}” redirectType=”Permanent” />
</rule>
–>
<!–
### Built-in filename-based cache busting
In a managed language such as .net you should really be using the internal bundler for css + js
or getCassette or similar.
If you’re not using the build script to manage your filename version revving,
you might want to consider enabling this, which will route requests for
/css/style.20110203.css to /css/style.css
To understand why this is important and a better idea than all.css?v1231,
read: github.com/h5bp/html5-boilerplate/wiki/Version-Control-with-Cachebusting
<rule name=”Cachebusting”>
<match url=”^(.+)\.\d+(\.(js|css|png|jpg|gif)$)” />
<action type=”Rewrite” url=”{R:1}{R:2}” />
</rule>
</rules>
</rewrite>–>
</system.webServer>
</configuration>
———————————————————————————
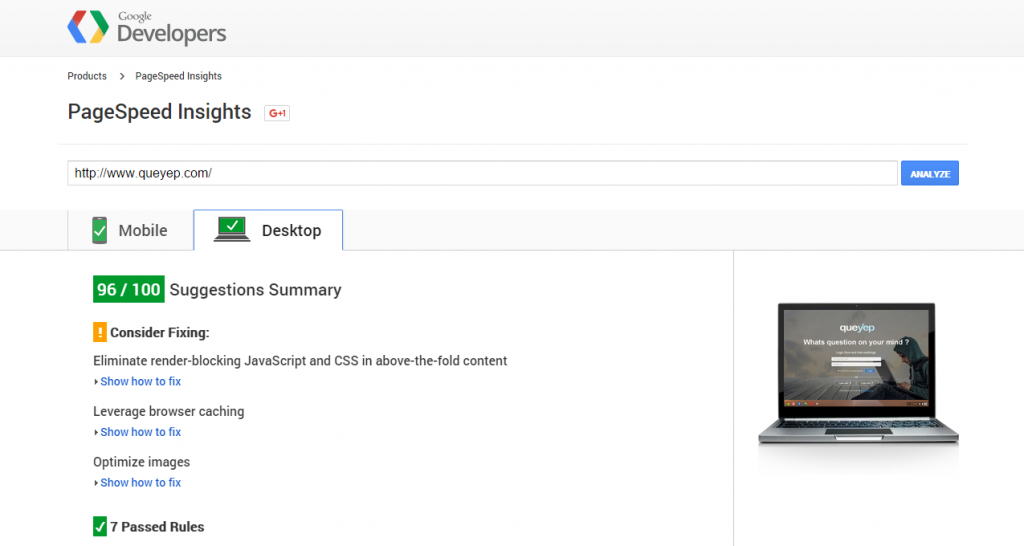
You can customize as per your requirement cache time limit ,and now you question,
What is gzip compression?
When a user hits your website a call is made to your server to deliver the requested files.
The bigger these files are the longer it’s going to take for them to get to your browser and appear on the screen.
Gzip compresses your webpages and style sheets before sending them over to the browser. This drastically reduces transfer time since the files are much smaller.
What is Caching?
Caching is a great example of the ubiquitous time-space tradeoff in programming. You can save time by using space to store results.
In the case of websites, the browser can save a copy of images, style-sheets, JavaScript or the entire page. The next time the user needs that resource (such as a script or logo that appears on every page), the browser doesn’t have to download it again. Fewer downloads means a faster, happier site.
Thanks
If you have any query then tell me


Greetings from Los angeles! I’m bored to tears at work so I decided to check out your website on my iphone during lunch break.
I really like the knowledge you provide here and can’t wait to take a look when I get home.
I’m shocked at how quick your blog loaded on my phone .. I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G ..
Anyhow, amazing site!
Thanks supreme,
It is part of content management and simpleness with above code … 🙂